Laser Micro-Processing (Ablation, Texturing and Functionalization)
Surface coloration and effects by laser micro-texturing
By applying controlled heat to metallic surfaces, oxide layers are formed, whose chemical composition and thickness result in coloration. This coloration can be combined with surface effects such as colour shifts or iridescence, which are produced by micro- and nanostructures, as well as redeposited nanoparticles
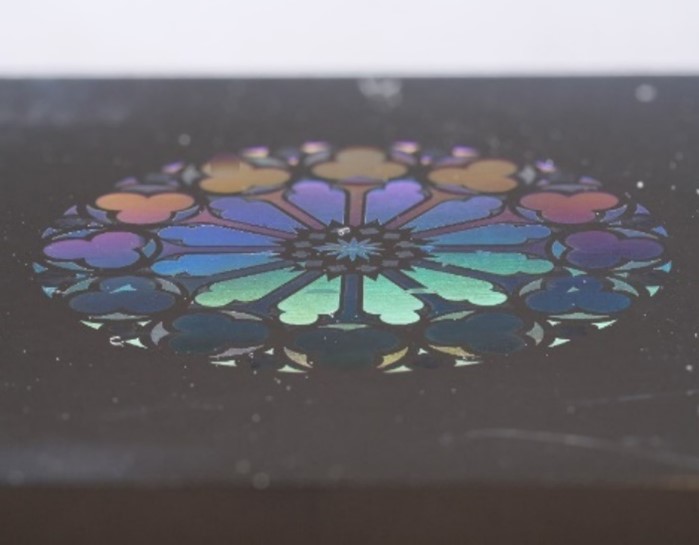

Applications:
• Anti-counterfeiting and security
• Branding and marking (logos, labels, luxury products)
• Decorative in jewellery
• Functional markings (blackening)
Research interests:
• Combination of colouring effects
• New applications, e.g. in technical and consumer products
• Anti-counterfeiting effects (through polarized light)
Contact:
external page Dr. Timo Schudeleit
Direct Laser Interference Patterning and optical beam path development
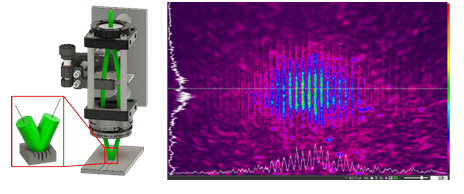
Applications:
• Functional surface inspired by nature
• Micro-texturing, engraving, cutting, drilling
• Integrate DLIP heads into scanner-based laser machines
• Inner texturing of bearings, channels, hydraulic cylinders
Research interests:
• Miniaturization of optics for simple machine integration
• New optics to texture difficult to access surfaces
• New functionalities for beam shaping (DLIP)
• Micro-texture optics for high resolution
Contact:
external page Dr. Timo Schudeleit
Tailored wettability by laser surface texturing
The wettability of a surface is dominantly influenced by its surface energy. It can be tailored to the specific need by micro- and nano-texturing. These textures can be produced by direct laser ablation and direct laser interference patterning to any kind of material.

Applications:
• Self-cleaning surfaces (solar-cells, glass),
• Improved adhesion (brazing, glueing, coatings)
• Lubrication of bearings
• Anti-icing (airplane wings), anti-corrosion, improved sealing
Research interests:
• Direct laser interference patterning (beam shaping)
• Hierarchical textures (combined micro- & nano-textures)
• Temperature dependent and long-term behavior
Contact:
external page Dr. Timo Schudeleit
3D micro-processing of transparent materials by ultra-fast pulsed laser
The wettability of a surface is dominantly influenced by its surface energy. It can be tailored to the specific need by micro- and nano-texturing. These textures can be produced by direct laser ablation and direct laser interference patterning to any kind of material.
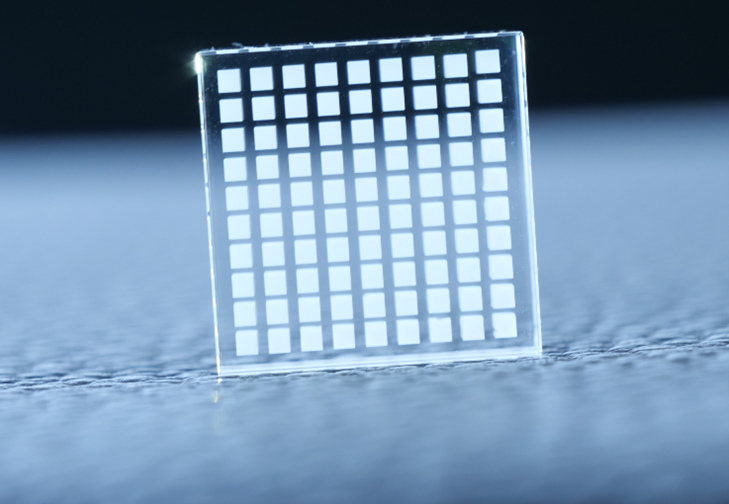
Applications:
• Micro-fluidics (MedTech)
• Aesthetics / anti-counterfeit (jewellery / luxury)
• Wave guides, anti-reflection (solar cells)
• Optics, micro-optics
Research interests:
• Nano/micro-laser texturing for diffractive optics elements and anti-reflection
• Colored engravings
Contact:
external page Dr. Timo Schudeleit
Ultra-hard cutting tools by 5-axis laser ablation
Ultrashort pulsed lasers, combined with advanced CAM solutions, are used to precisely shape complex cutting tools from both bindered and binderless materials such as diamond, cBN, or WC. The process delivers high resolution and exhibits no tool wear, resulting in superior accuracy and surface finish. This technology enables the creation of innovative tool geometries that significantly outperform ground tools in terms of both lifespan and productivity. For small and micro-tools, laser fabrication offers higher productivity and lower scrap rates compared to traditional grinding methods.

Applications:
• Turning, drilling and milling tools made of ultra-hard materials for WC, ceramics, composites, and titanium machining
• Micro-tools for electrodes machining, watch making, microelectronics
Research interests:
• Process development novel tool materials and
• Novel tool geometries
• Micro-tool production by micro-scanners
• In-situ and closed loop inspection and correction cycle
Contact:
external page Dr. Timo Schudeleit